Introduction
This article provides an in-depth examination of the architecture for Leena AI’s enterprise Agentic AI. It demonstrates how different layers and components interconnect to deliver AI Agents with human-like agency.
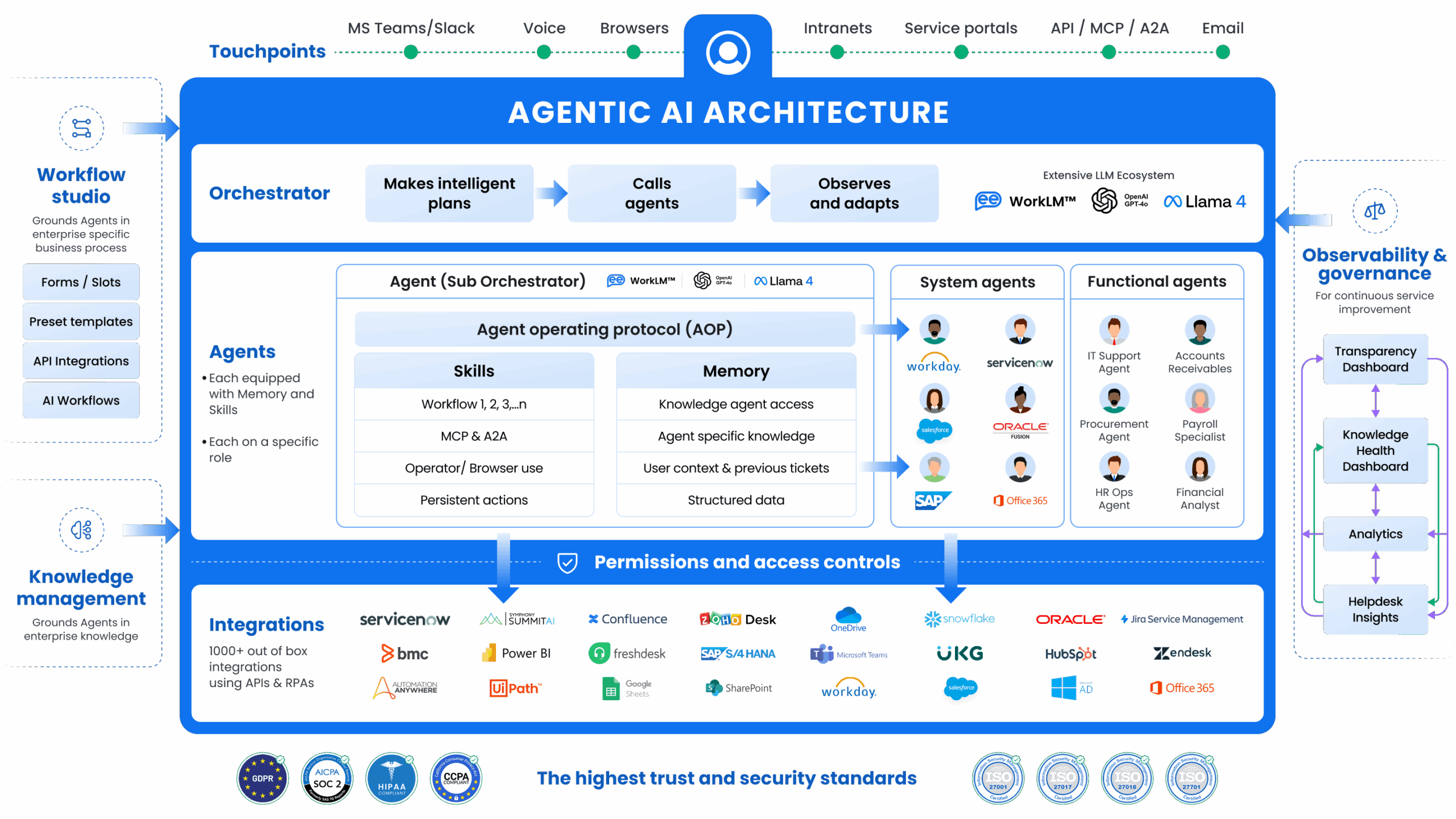
Above is a comprehensive description of the Leena AI “Agentic AI Architecture” diagram, breaking down each component and illustrating how they interact to form a cohesive enterprise AI solution.
The Architecture Highlights:
- Touchpoints: Channels where users interact with the Agentic AI systems
- Orchestrator: Central planning and coordination engine
- Agents: Specialized AI agents based on roles or systems
- Workflow Studio: To ground the Agentic system in Business Processes
- Knowledge Management: Central repository of organizational knowledge
- Permissions & Access Controls: Security layer ensuring compliance and role-based access
- Observability and Governance: Oversight, governance, and continuous improvement
- Security & Compliance: Adherence to industry standards like HIPAA, GDPR, SOC2, etc.
1. Touchpoints
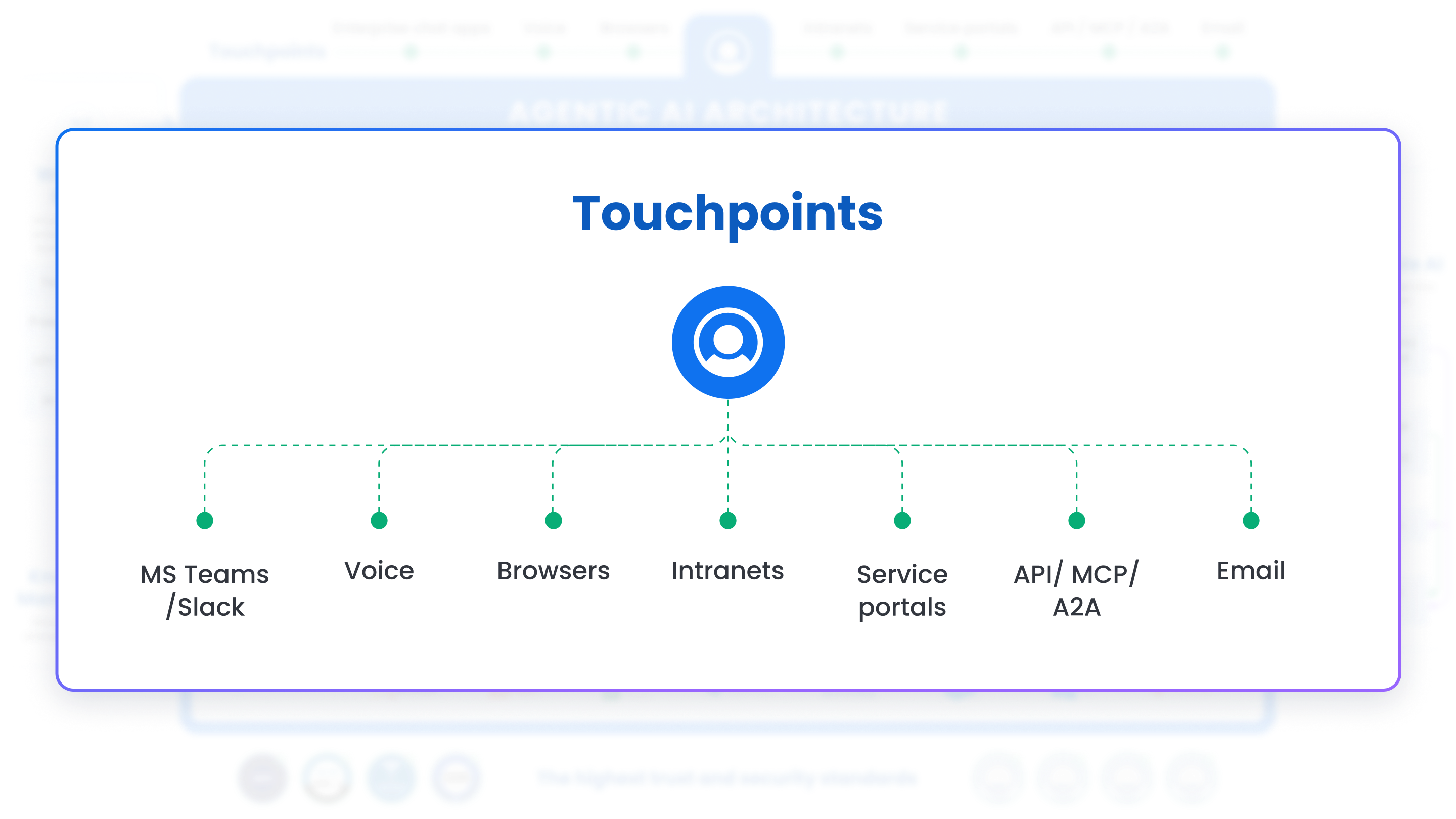
Positioned at the top of the diagram are multiple touchpoints through which users and systems can interact with the AI Agents:
- Web Chat
- Voice
- SMS
- Messaging Apps (e.g., Microsoft Teams, Slack, Zoom, WhatsApp)
- API, MCP, A2A (for invoking agents on different types of triggers), and interoperability
- Intranet (internal company portals
These touchpoints represent the diverse channels used by employees or partners to engage with the Agents. The architecture is channel-agnostic, meaning any new channel can be integrated with minimal overhead.
2. Orchestrator
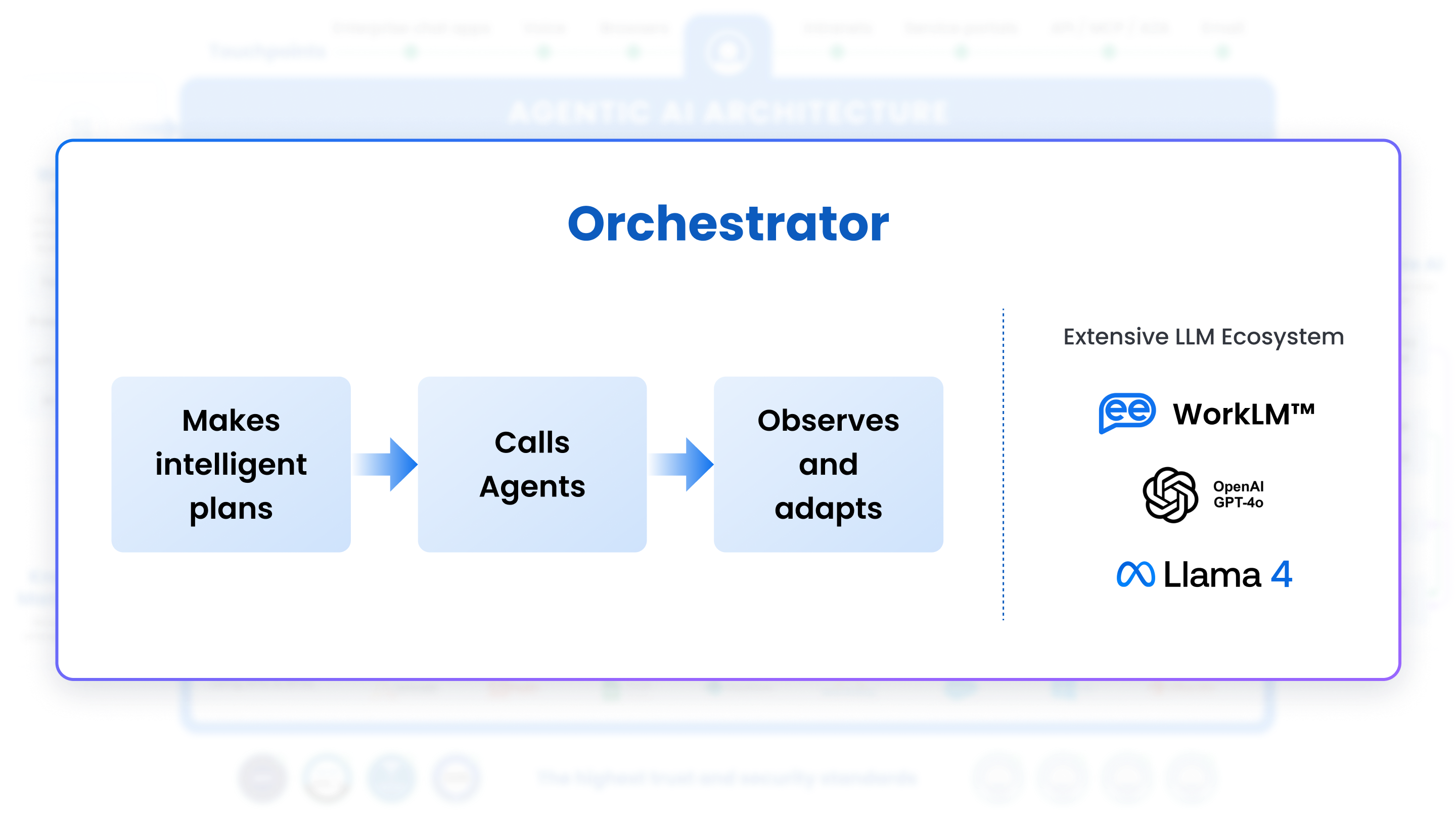
At the core of the architecture is the Orchestrator, a centralized engine responsible for:
- Receiving Requests: From any of the touchpoints, the Orchestrator captures incoming queries, tasks, or requests.
- Intelligent Planning: The Orchestrator determines the sequence of actions or “plan” needed to fulfill each request. This can include identifying which Agents or services are needed.
- Calling Agents: Once the plan is set, the Orchestrator dispatches tasks to the appropriate Agent(s). It also monitors progress, handles dependencies & errors, and aggregates results.
The Orchestrator ensures that requests are routed efficiently and that the right domain agent is engaged for each task. The orchestrator leverages multiple LLMs, including Leena AI’s proprietary WorkLM (powered by the Mixtral 8x22B and finetuned on 2 TB+ of proprietary enterprise data), Gemini models for multimodal capabilities, Claude models for higher complexity & reasoning prompts & OpenAI models for low latency requirements. The architecture is modular, ensuring newer models can be quickly plugged in for testing.
3. Agents
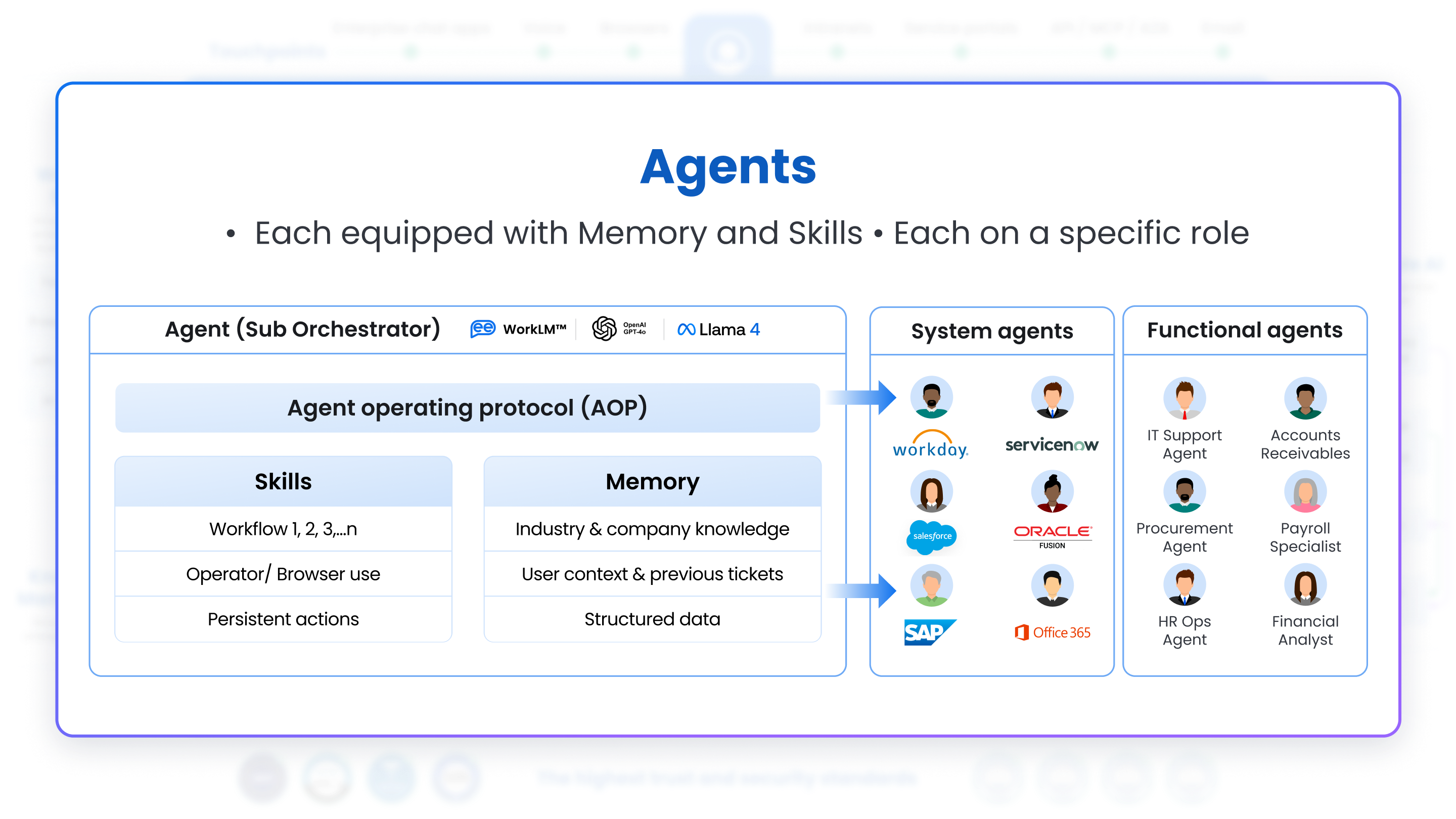
Directly under the Orchestrator, you see Agents: self-contained AI modules or services that handle specific tasks with agency. Key points about these Agents:
Integration with LLM Ecosystem
- Agents can be powered by or integrated with Large Language Models (LLMs) such as GPT-3/o1, Anthropic Claude 3.7, Gemini, LLaMA, or other foundational models.
- The choice of LLM can be dynamic based on the use case, data sensitivity, or performance requirements.
Agent Operating Procedure (AOP)
AOP is to agents what SOP is to humans. AOP grounds the agent in your company’s Business Processes, for eg, the PO creation agent has to follow your company’s specific PR creation, approval, and then PO creation process. AOPs allow Agents to “ingest” detailed process maps (text, flow charts) and follow the Business Process at run-time without having to create complex, resource-intensive workflows. These can simply be your existing SOPs or Business Process Flow Diagrams, or even just written text.
Specialized Skills & Memory
Each Agent is equipped with the domain expertise required to solve certain types of problems—whether HR, IT, Finance, or something else. Each Agent is an Orchestrator in itself and might be using different base LLMs as required by the role of that agent.
◦ An example of an agent can be:
‣ IT Helpdesk Agent who has domain knowledge and knows how to use relevant tools to solve employee IT problems.
‣ Account Payable (AP) Analyst who has domain knowledge and knows how to use relevant tools to seamlessly pay and reconcile payments.
◦ Skills of an agent are Enterprise-specific Workflows, which are configured in the Workflow Studio. Each agent has access to multiple Workflows. Customers can configure templates available in the Workflow Studio according to their needs to quickly get up and running. This is extremely important because you need to ground the Agent into every company’s deterministic business processes.
‣ Apart from these skills, which are configured to align with Customers’ business processes, every agent also has out-of-the-box skills like Computer Use, Coding, Comparison, etc.
◦ The memory of an agent is external knowledge it has access to (or fine-tuned on), Company-specific structured/unstructured knowledge like Process guides, how-tos, etc. All of these are made available to the Agent via the Knowledge Agent.
◦ A single agent can be invoked either by the orchestrator or by an API, too.
If an agent needs help from another agent, it will go back to the orchestrator and ask for that help. In the future, we plan to allow for agent-to-agent communication directly too.
Integrations
Each agent is typically integrated with relevant third-party systems or databases (ServiceNow, Salesforce, BambooHR, Zendesk, Coupa, Snowflake, Confluence, and so on) to facilitate end-to-end process automation. The Agents interact with these applications to retrieve or update data, orchestrating multi-step processes across the enterprise.
Agents form the backbone of the system’s intelligence—modular, specialized, and easily updatable as new models or technologies become available.
4. Workflow Studio
Skills of an agent are Enterprise-specific deterministic Workflows, which are configured in the Workflow Studio. Each agent has access to multiple Workflows. Customers can configure templates available in the Workflow Studio according to their needs to quickly get up and running. This is extremely important because you need to ground the Agent into every company’s specific business processes.
The Workflow Builder comes out of the box with over 5000+ pre-built templates across 1000+ enterprise application integrations, including Workday, SAP, ServiceNow, Salesforce, Oracle, UKG, etc.
Know more about Workflow Studio here
5. Knowledge Management

The memory of an agent is external knowledge it has access to (or fine-tuned on), Company-specific structured/unstructured knowledge like Process guides, how-tos, etc, or even examples of how to do things. All of these are made available via the Knowledge Agent.
KM has out-of-the-box integrations with:
- Enterprise knowledge management apps like SharePoint, ServiceNow KM, Box, Drive, Dropbox, etc.
- Data lakes like Snowflake, Databricks, Azure S3, etc
- Scraping capabilities – you can point it to scrape any website that you want to add to your company’s Knowledge.
We integrate and sync all knowledge into Leena AI Knowledge Management (KM) to find the right knowledge at inference time quickly, since applications APIs can be slow. All enterprise knowledge is synced into Leena AI and regularly pre-processed to make information readily available to the agent. Leena AI KM also maintains security groups of all knowledge articles from all knowledge sources to ensure secure and permission-appropriate access to knowledge. Read more about pre-processing here
6. Permissions & Access Controls
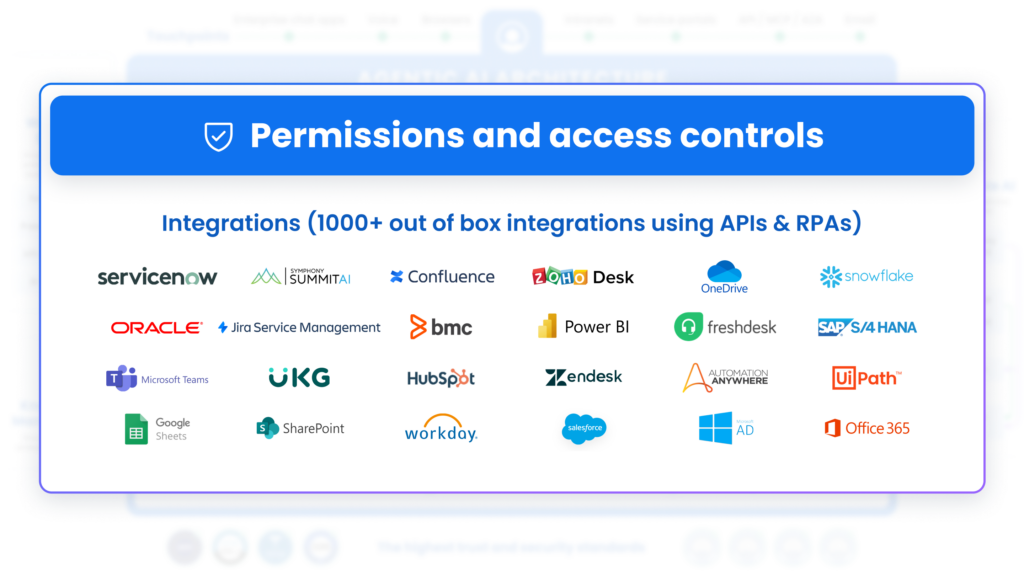
In the center, bridging the Domain-Specific Modules, there is a robust Permissions & Access Controls layer. This ensures:
- Role-Based Access: Only authorized individuals or systems can view or modify specific data.
- Security & Compliance: The system respects regulations like ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR, and SOC2, maintaining data privacy and integrity.
- Multi-Tenant Architecture: If the platform is deployed for multiple departments or organizations, each tenant’s data and workflows are securely isolated.
7. Observability and Governance – Responsible AI

Leena AI’s Responsible AI framework governs continuous service improvement and ensures ethical, compliant use of AI. It includes:
- Transparency Dashboard: Shows how decisions are made, providing traceability and explainability for AI-driven actions
- Knowledge Health Dashboard: When you integrate your Enterprise Knowledge into Leena AI KM, the Knowledge Health Dashboard will highlight issues in your Knowledge like overlapping knowledge, stale knowledge, absent security groups, etc. This is extremely important to avoid Garbage-in/Garbage-out.
- Analytics: Monitors system performance, user interactions, and Agent accuracy. It may also track key performance indicators (KPIs) and usage metrics.
- Helpdesk Insights: Analyzes user queries, identifies trends, and recommends improvements to workflows or the Knowledge Base.
This layer helps organizations comply with internal governance policies and external regulations while maintaining user trust.
8. Security & Compliance

Leena AI is used by over 500+ enterprises globally and has various industry certifications and compliance with many regulations:
- HIPAA: Ensuring healthcare data privacy
- GDPR: European data protection requirements
- SOC2: Service Organization Control for data security and privacy
- ISO 27001: International standard for information security management.
Other standards or certifications may be relevant depending on the specific industry or geographical location. The system is designed to be private and compliant, with data encryption, secure data handling, and audit trails.
Conclusion
Leena AI’s Agentic AI Architecture is designed to provide an end-to-end solution for enterprise-grade AI services. By combining a central Orchestrator, specialized Agents, the Workflow Studio, Knowledge Base, and out-of-the-box integrations, organizations can automate complex processes across different domains while maintaining strict security, compliance, and ethical standards. The incorporation of a Responsible AI framework ensures transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement—key factors for successful AI adoption in modern enterprises. Learn More here!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Agentic AI
1. What is the core “agentic definition” when we talk about AI?
A: In the context of AI, the “agentic definition” refers to an AI system’s capacity for agency. This means the AI can perceive its environment, make independent decisions, and take autonomous actions to achieve specific goals. It’s about AI moving beyond passive responses to become an active participant in processes.
2. Can you give a simple “Agentic AI definition”? What is Agentic AI in essence?
A: Essentially, Agentic AI is an advanced form of artificial intelligence that doesn’t just answer questions or provide information, but actively performs tasks and completes actions on behalf of users. The Agentic AI definition emphasizes its ability to combine knowledge with action to get things done across various enterprise systems.
3. How does Agentic AI differ from generative AI?
A: While both are advanced AI, Agentic AI is primarily focused on action and task completion within enterprise systems, guided by specific workflows and goals. Generative AI, on the other hand, excels at creating new content (text, images, code). An Agentic AI system might use generative AI capabilities as one of its tools, but its core purpose is to act as an intelligent agent that executes tasks.
4. “What is an agentic workflow” and how do “agentic AI workflows” help businesses?
A: An agentic workflow is a defined sequence of steps, decisions, and actions that an Agentic AI system follows to complete a specific business process. These agentic AI workflows help businesses by automating complex, often multi-system tasks (like employee onboarding or IT support resolution), ensuring consistency, improving efficiency, and freeing up human employees for more strategic work.
5. What are “Agentic AI frameworks” and why are they important for deploying Agentic AI?
A: Agentic AI frameworks refer to the comprehensive architecture and underlying structure that enables Agentic AI to operate effectively, reliably, and securely within an enterprise. This framework typically includes components like an orchestrator, specialized agents, a workflow studio, knowledge management systems, integration layers, and robust security and permission controls. They are important because they provide the necessary foundation for scalable, manageable, and “future-proof” Agentic AI solutions.
6. What are the key benefits of implementing Agentic AI in an enterprise?
A: Implementing Agentic AI offers several key benefits, including: * Enhanced employee experience by providing a single, intelligent point of contact for tasks and information, reducing confusion from too many apps. * Increased productivity by automating routine tasks and handling complex cross-system use cases. * Improved operational efficiency by streamlining processes across various departments like HR, IT, and Finance. * Reliable and trusted assistance, as enterprise-grade Agentic AI is designed to avoid hallucinations and follow strict data permissions.
7. How do “agentic AI workflows” specifically improve the employee experience?
A: Agentic AI workflows improve the employee experience by making interactions with company systems seamless and intuitive. Instead of employees needing to know which system to use for a specific task (e.g., requesting leave, resolving an IT issue), the Agentic AI, guided by its workflows, handles these processes behind the scenes. This means employees get their tasks done quickly and easily, reducing frustration and allowing them to focus on their core responsibilities.







2 Comments