
Artificial Intelligence (AI), especially Generative AI, has changed how businesses work by making it so easy to streamline and improve daily tasks in ways never possible before. This new technology makes business processes more efficient and makes the lives of employees and employers easier. The world of Generative AI offers many use cases in a business today, opening up many new possibilities while also increasing the level of responsibility.
With great power comes with great responsibility! This is also true in the case of Generative AI implementation.
It is important for businesses to realize that if customer data is mishandled, information is changed, or privacy is broken, both customers and service providers can face serious problems. As a result, organizations must take proactive steps to set up clear rules, ethical guidelines, and strong security protocols, all with the goal of stopping AI from being used wrongly. And encouraging responsible AI practices in the workplace. In this blog, we will go over how organizations should ensure that AI technologies are used responsibly and in the best interests of everyone involved.
Let’s begin….
Responsible AI at the Workplace: Understanding the Benefits and Risks
Every new technology has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Similarly, integrating Generative AI with existing business processes has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Before using any new technology, it is critical to grasp both sides of the coin. In the table below, we list some of the risks and rewards that you ought to consider about before deploying Generative AI in your business.
|
Positive Impacts of AI Implementation |
Risks and Challenges of AI Implementation |
|
Improved Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide instant and personalized customer support, addressing queries and providing recommendations. This enhances the customer experience by reducing response times and increasing customer satisfaction. |
Data Privacy and Security: Data privacy in AI involves collecting and analyzing large amounts of personal data. Organizations must ensure robust data protection measures to safeguard sensitive information and prevent privacy breaches. |
|
Streamlined Operations: AI automation can optimize routine tasks, streamline processes, and improve operational efficiency. |
Ethical Considerations: AI systems may inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to discriminatory outcomes. It is essential to design and monitor AI systems to mitigate biases and ensure fairness and equality. |
|
Enhanced Decision-Making: AI algorithms can process and analyze vast amounts of data, providing insights and recommendations for informed decision-making. |
Workforce Adaptation: AI automation may lead to job displacement or require employees to acquire new skills. Organizations must plan for workforce adaptation, providing reskilling and upskilling opportunities to employees affected by AI implementation. |
|
Improved Safety and Risk Management: AI can detect anomalies, monitor conditions, and predict potential risks, enhancing workplace safety and risk management strategies. |
Lack of Transparency: Complex AI algorithms, such as deep learning models, can be difficult to interpret and understand. This lack of transparency may raise concerns about the ability to explain AI-generated decisions or predictions, limiting trust and acceptance of AI systems. |
|
Innovation and New Opportunities: AI enables organizations to innovate and create new products, services, and business models. By leveraging AI technologies, companies can explore novel ways to solve problems, gain a competitive edge, and unlock new opportunities for growth and value creation. |
Integration Challenges: Implementing AI technologies may require significant changes in existing infrastructure, data systems, and workflows. Integration challenges, including compatibility issues and resistance to change, can hinder the successful implementation of AI initiatives. |
|
Regulatory Compliance: Organizations must navigate legal and ethical frameworks governing AI use, such as data protection regulations, to ensure compliance. Failure to comply with regulations can lead to legal consequences and reputational damage. |
|
|
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: AI can automate repetitive tasks, streamline workflows, and handle data analysis at scale. This leads to improved productivity, faster task completion, and optimized resource allocation. |
Cost and Resource Intensiveness: Implementing AI technologies can be resource-intensive, requiring significant investments in infrastructure, data management, and talent acquisition. Organizations must carefully assess costs and allocate resources to ensure sustainable implementation. |
|
Impact on Decision-Making: Relying solely on AI-generated insights and recommendations without human judgment and expertise may limit |
|
|
Unintended Consequences: AI systems may produce unintended outcomes or unexpected behaviors, leading to unforeseen consequences. Thorough testing, monitoring, and ongoing evaluation are necessary to identify and mitigate such risks, ensuring the safe and responsible use of AI. |
The Key Principles of Responsible AI at the Workplace
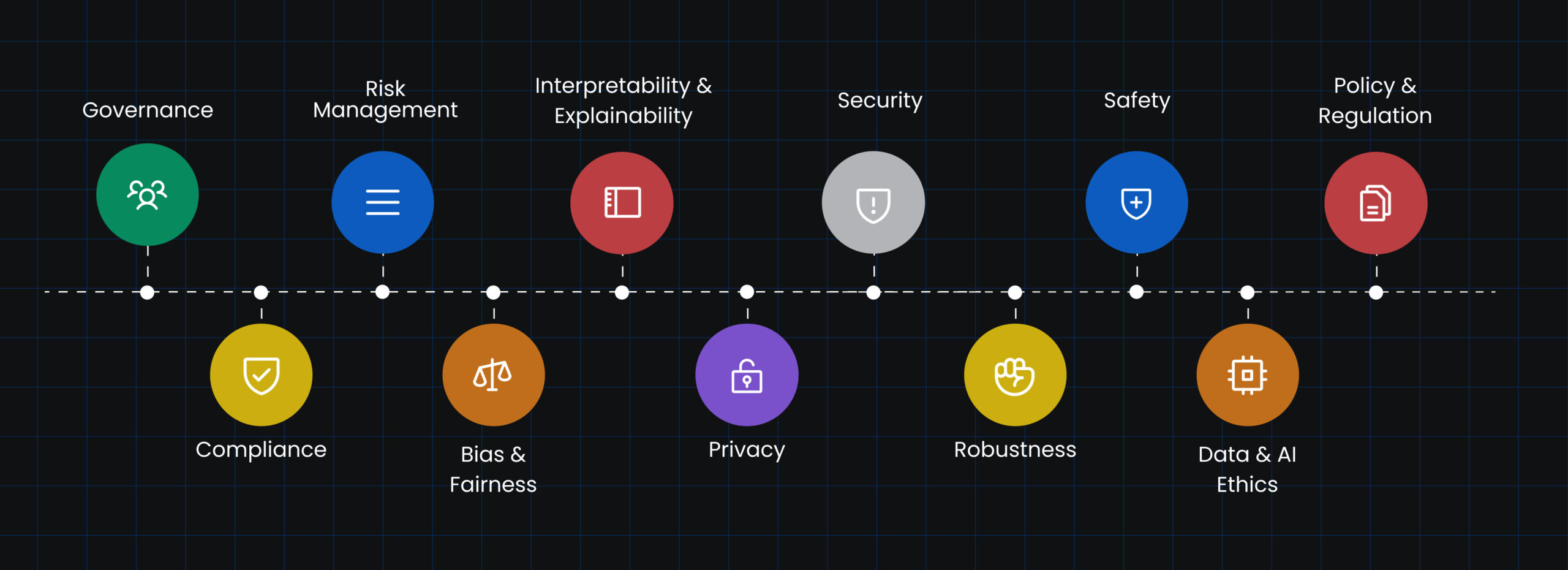
Before incorporating Generative AI into their operations, organizations should establish their own set of rules and norms. However, if you are new to this area of technology, we have outlined a few generic ethical AI practices below to get you started. Organizations that follow these Responsible AI practices can assure the ethical, transparent, and beneficial use of AI technology while minimizing dangers and maximizing AI’s positive influence on society.
 Governance:
Governance:
Governance refers to the establishment of clear lines of accountability and responsibility for AI systems within organizations. It involves defining roles and responsibilities, setting up processes for decision-making, and ensuring transparency in AI-related activities. Effective AI governance helps ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed in an ethical and responsible manner.
 Compliance:
Compliance:
Compliance involves adhering to legal and regulatory requirements related to AI. Organizations must consider laws and regulations concerning data protection, privacy, and fairness in their AI practices. Compliance with these regulations helps mitigate risks and ensures that AI systems are developed and used in a manner that respects legal and ethical boundaries.
 Risk Management:
Risk Management:
Risk management involves identifying and mitigating potential risks associated with AI systems. This includes assessing risks related to bias, security breaches, privacy violations, and unintended consequences. Organizations should develop strategies to minimize these risks and have processes in place to monitor and address any emerging risks throughout the AI system’s lifecycle.
 Bias & Fairness:
Bias & Fairness:
Bias and fairness address the potential for discriminatory outcomes in AI systems. It is crucial to ensure that AI algorithms and data do not perpetuate or amplify biases based on protected attributes such as race, gender, or ethnicity. Organizations should strive to design and train AI systems to be fair, transparent, and unbiased, conducting regular audits and evaluations to detect and mitigate bias.
 Interpretability & Explainability:
Interpretability & Explainability:
Interpretability and explainability focus on making AI systems more understandable and transparent. Organizations should strive to develop AI models and algorithms that can provide explanations for their decisions or predictions. This promotes trust, enables better accountability, and helps identify and rectify any potential errors or biases.
 Privacy:
Privacy:
Privacy is about safeguarding personal data collected and used by AI systems. Organizations must handle data responsibly, ensure informed consent for data collection and usage, and implement appropriate data protection measures. Privacy considerations include data anonymization, secure data storage, and compliance with relevant privacy laws and regulations.
 Security:
Security:
Security involves protecting AI systems and data from unauthorized access, manipulation, or breaches. Organizations should implement robust security measures to safeguard AI infrastructure, prevent data breaches, and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data used by AI systems. This includes regular security audits, encryption, access controls, and incident response plans.
 Robustness:
Robustness:
Robustness refers to the reliability and resilience of AI systems. It involves ensuring that AI models are capable of performing accurately and consistently across various scenarios and datasets. Robustness testing, validation, and ongoing monitoring are necessary to detect and address any limitations, vulnerabilities, or performance issues.
 Safety:
Safety:
Safety focuses on ensuring that AI systems operate without causing harm to users, employees, or the broader society. Organizations must assess and mitigate potential risks associated with AI technologies, particularly in safety-critical domains such as autonomous vehicles or healthcare. Emphasizing safety considerations helps prevent accidents, minimize errors, and instill trust in AI systems.
 Data & AI Ethics:
Data & AI Ethics:
Data and AI ethics emphasize responsible and ethical practices throughout the AI lifecycle. This includes responsible data collection, data governance, and ethical considerations in algorithm design and decision-making processes. Organizations should uphold principles of transparency, fairness, and accountability to ensure ethical use of data and AI technologies.

 Policy & Regulation:
Policy & Regulation:
Policy and regulation encompass the development and implementation of laws, guidelines, and ethical frameworks that govern AI technologies. Policymakers and regulators play a crucial role in addressing potential risks, ensuring accountability, and setting legal and ethical boundaries for AI deployment. Clear policies and regulations promote responsible AI practices and protect societal interests.
Establishing Responsible AI Frameworks in Organizations
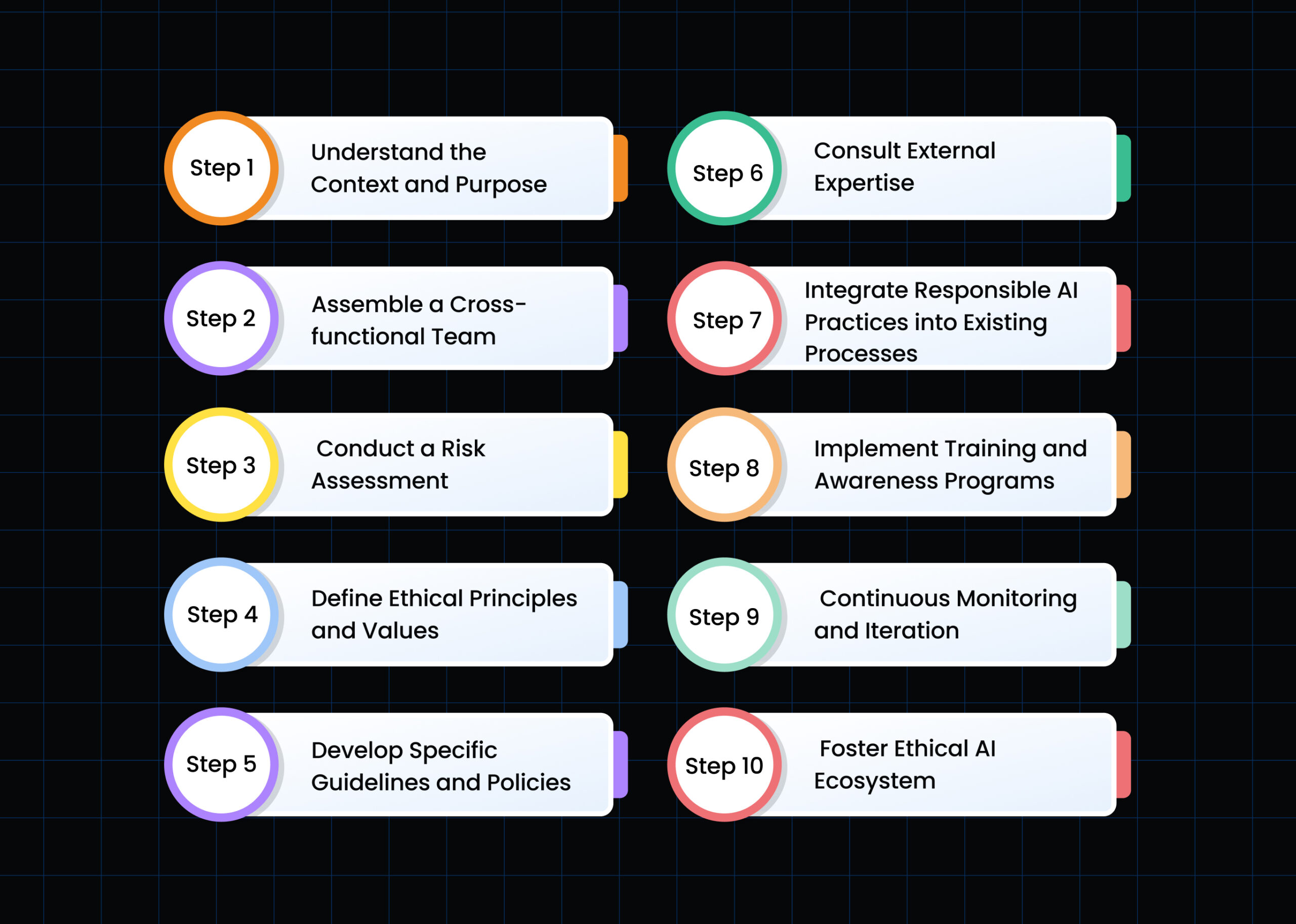
Now that you know what ethical AI practises should be, the next step is to figure out how to incorporate them into your existing procedures. Establishing Responsible AI guidelines and regulations, as well as integrating Responsible AI practises into current processes, requires a methodical and deliberate approach. Here’s a full step-by-step guide to accomplishing this:
Step 1: Understand the Context and Purpose
Before diving into the development of Responsible AI guidelines and policies, it’s crucial to understand the context in which the AI system will be deployed and the purpose it aims to serve. Consider the organization’s values, industry standards, legal and regulatory requirements, and the specific ethical concerns associated with AI technology.
Step 2: Assemble a Cross-functional Team
Form a cross-functional team that represents diverse perspectives and expertise. This team should include individuals from various departments, such as legal, compliance, IT, data science, ethics, and business stakeholders. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the organizational context and helps identify potential ethical risks and considerations.
Step 3: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Perform a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential ethical, legal, and societal risks associated with the AI system. This assessment should consider factors such as data privacy, bias and fairness, transparency and explainability, accountability, and potential social impact. Identify the stakeholders who might be affected by the AI system and take their perspectives into account.
Step 4: Define Ethical Principles and Values
Based on the risk assessment, establish a set of ethical principles and values that will guide the development, deployment, and use of AI systems. These principles should align with the organization’s mission and values while addressing the identified risks. Common ethical principles include fairness, transparency, accountability, privacy, and human-centeredness.
Step 5: Develop Specific Guidelines and Policies
Translate the ethical principles and values into specific guidelines and policies that provide practical guidance for AI development and usage. These guidelines should be actionable and cover areas such as data collection and usage, algorithm development and validation, bias detection and mitigation, interpretability and explainability, privacy protection, and governance and accountability frameworks.
Step 6: Consult External Expertise
Consider seeking input from external experts in AI ethics, legal and regulatory domains, or independent ethics boards. This external perspective can help identify blind spots and ensure that the guidelines and policies address a wide range of ethical concerns.
Step 7: Integrate Responsible AI Practices into Existing Processes
To integrate responsible AI practices into existing processes, identify the relevant stages where AI is used, such as data collection, model development, deployment, and monitoring. Review and modify existing processes to align with the ethical guidelines and policies. This may involve incorporating new checks and balances, introducing transparency mechanisms, implementing fairness assessments, or creating data governance frameworks.
Step 8: Implement Training and Awareness Programs
Develop training and awareness programs to educate employees and stakeholders about ethical guidelines, policies, and responsible AI practices. These programs should cover topics such as AI ethics, bias detection and mitigation, privacy protection, and the social impact of AI. Foster a culture of responsibility and accountability throughout the organization.
Step 9: Continuous Monitoring and Iteration
Establish a feedback loop to continuously monitor and evaluate the AI system’s impact and adherence to ethical guidelines. Regularly review and update the guidelines and policies based on feedback, evolving technologies, and changes in the regulatory landscape. Ensure that the ethical considerations keep pace with emerging challenges and best practices in the field.
Step 10: Foster Ethical AI Ecosystem
Collaborate with other organizations, academia, and industry associations to foster an ethical AI ecosystem. Share best practices, engage in public discourse, and contribute to the development of industry-wide standards and frameworks. By actively participating in the broader AI community, organizations can collectively work towards responsible and ethical AI practices.
Understanding How To Promote the Culture of Responsible AI at the Workplace
So far, you must have realised that the responsible use of AI in the workplace is of utmost importance. And, creating a culture that embraces and upholds fair AI practices is crucial for organizations to mitigate risks, ensure fairness, and build trust with employees, customers, and stakeholders. In this section, we will explore key strategies to promote a culture of responsible AI at the workplace.
 Leadership Commitment:
Leadership Commitment:
Fostering a culture of responsible AI starts at the top. Leadership commitment is essential to set the tone and demonstrate the organization’s dedication to ethical practices. Executives should openly prioritize responsible AI, endorse the development and implementation of guidelines and policies, and allocate resources for training, monitoring, and continuous improvement.
 Education and Awareness Programs:
Education and Awareness Programs:
To create a culture of responsible AI, it is vital to educate employees at all levels about the ethical implications of AI technology. Develop comprehensive training programs that cover topics such as AI ethics, bias detection and mitigation, privacy protection, and the societal impact of AI. Encourage ongoing learning and provide resources for employees to stay updated on emerging AI-related ethical issues.
 Employee Involvement and Engagement:
Employee Involvement and Engagement:
Promote employee involvement in shaping responsible AI in HR. Establish mechanisms for employees to provide feedback, share concerns, and participate in ethical decision-making processes. Encourage open dialogue and create a safe space for employees to voice their opinions and contribute to the organization’s responsible AI solutions. Recognize and reward employees who demonstrate a commitment to responsible AI practices.
Learn about Syngenta’s journey toward employee collaboration and upskilling here:

 Ethical Guidelines and Policies:
Ethical Guidelines and Policies:
Develop and communicate clear ethical guidelines and policies that govern the use of responsible AI toolkit. Ensure these guidelines cover areas such as data privacy, bias and fairness, transparency and explainability, accountability, and human-centeredness. Involve employees in the development and review process to enhance their sense of ownership and alignment with ethical principles.
 Transparency and Explainability:
Transparency and Explainability:
Promote transparency and explainability in AI systems and decision-making processes. Encourage the use of interpretable models and algorithms to help employees understand how AI-driven decisions are made. Foster a culture of openness and encourage employees to ask questions and seek clarification on AI systems’ functioning and potential biases.
 Accountability and Governance:
Accountability and Governance:
Establish clear lines of accountability and governance for responsible AI practices. Assign roles and responsibilities for monitoring and ensuring compliance with ethical guidelines. Implement mechanisms for regular audits and evaluations to assess the impact of AI systems on employees, customers, and society. Foster a culture of shared responsibility, where employees understand their roles in upholding ethical AI practices.
 Continuous Learning and Improvement:
Continuous Learning and Improvement:
Recognize that responsible AI practices are an ongoing journey. Encourage a culture of continuous learning, improvement, and adaptation to emerging ethical challenges. Regularly review and update ethical guidelines and policies to reflect evolving technologies and societal expectations. Promote collaboration and knowledge sharing across teams and departments to drive the most of responsible AI impact.
Conclusion:
To sum up, Responsible AI practices are vital for creating a workplace environment that upholds ethical standards, mitigates risks, and builds trust. By prioritizing responsible AI, organizations can harness the power of AI technology while ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Promoting a culture of responsible AI starts with leadership commitment and the development of clear ethical guidelines and policies. Educating employees about AI ethics, fostering employee involvement, and establishing transparency and explainability are key strategies for creating a responsible AI culture.
Looking into the future, ethical AI by design will become the norm, embedding responsible practices throughout the development lifecycle. Human-AI collaboration will empower employees and enhance productivity, while continuous ethical assessments will ensure ongoing compliance and address emerging challenges.
Regulatory frameworks and industry-wide standards will shape responsible AI practices, requiring organizations to stay updated and adapt accordingly. Collaboration and knowledge sharing among organizations and industries will foster collective efforts to tackle ethical issues and drive responsible AI adoption.
In embracing responsible AI at the workplace, organizations pave the way for a future where AI technology aligns with ethical values, and benefits employees, customers, and society as a whole. By committing to responsible AI practices, organizations not only protect against risks but also foster a culture of trust, innovation, and long-term success in the era of AI.






